This article is about single-variable quadratic equations and their solutions. For more general information about the single-variable case, see Quadratic function.
- For the case of more than one variable, see Conic section or Quadratic form.
In elementary algebra, a quadratic equation (from the Latin quadratus for "square") is any equation having the form
where x represents an unknown, and a, b, and c represent known numbers such that a is not equal to 0. If a = 0, then the equation is linear, not quadratic. The numbers a, b, and c are the coefficients of the equation, and may be distinguished by calling them, respectively, the quadratic coefficient, the linear coefficient and the constant or free term.[1]
Because the quadratic equation involves only one unknown, it is called "univariate". The quadratic equation only contains powers of x that are non-negative integers, and therefore it is a polynomial equation, and in particular it is a second degree polynomial equation since the greatest power is two.
Source : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quadratic_equation

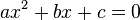


0 comments:
Post a Comment